Index Surge: Amplifying Your Insights
Stay updated with the latest trends and news across various industries.
Decoding the Search Intent Labyrinth
Unlock the secrets of search intent! Dive into our guide and navigate the labyrinth to boost your traffic and engagement today!
Understanding the Different Types of Search Intent: A Comprehensive Guide
Search intent, also known as user intent, is a critical concept in SEO that helps to understand what users are truly looking for when they input queries into search engines. There are four primary types of search intent: transactional, informational, navigational, and commercial investigation. Transactional intent refers to users who are ready to purchase a product or service. For example, someone searching for 'buy running shoes' is indicating a clear intention to complete a transaction. In contrast, informational intent involves users seeking knowledge or answers, such as someone entering 'how to tie running shoes,' indicating a desire for information rather than a purchase.
Understanding these different types of search intent can significantly enhance your content strategy. By tailoring your content to meet users' needs based on their intent, you can improve your website's visibility and engagement. For instance, content targeting navigational intent should be constructed to help users find specific websites or locations, like someone searching for 'Nike official website.' On the other hand, commercial investigation focuses on users who are comparing products or services, such as 'best running shoes for joggers,' and providing in-depth comparisons can effectively cater to this intent. A comprehensive understanding of search intent not only boosts your SEO but also creates a more fulfilling user experience.
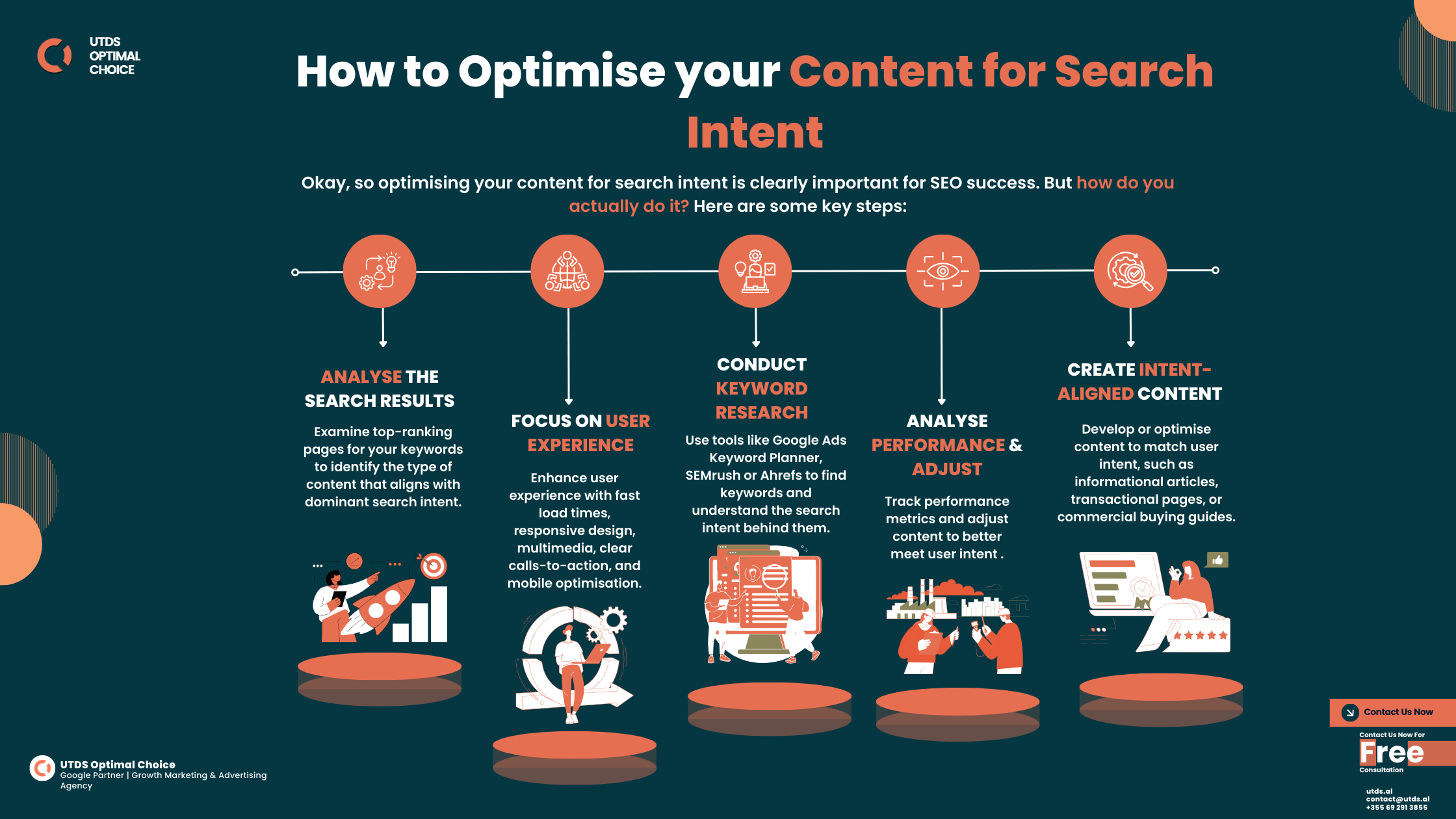
How to Optimize Your Content for User Intent in SEO
Optimizing your content for user intent is crucial in the world of SEO. User intent refers to the purpose behind a user's search query, whether they're looking for information, wanting to make a purchase, or seeking to navigate to a specific site. To effectively meet this intent, it's essential to conduct thorough keyword research to identify which terms and phrases your target audience is using. This can involve using tools to analyze search volume and competition, as well as examining search engine results pages (SERPs) for the types of content ranking well for those keywords.
Once you have a clear understanding of user intent, you can structure your content accordingly. Consider breaking down your content into sections that cater to different types of queries, such as informational, transactional, and navigational intents. Utilize header tags (H1, H2, H3) to organize your content and make it more scannable. Additionally, including visual elements like images, infographics, or videos can enhance user engagement, helping to fulfill their intent more effectively. Remember, delivering high-quality, relevant content that aligns with user intent will not only improve your SEO ranking but also foster trust and authority in your niche.
Decoding Search Intent: What Do Users Really Want?
Understanding search intent is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their content for search engines. Users often turn to search engines with specific goals in mind, whether it be to find information, make a purchase, or seek out professional services. By categorizing these intents into informational, transactional, navigational, and commercial investigation, content creators can tailor their strategies to address the exact needs of their audience. For instance, a user searching for 'how to bake a cake' is likely looking for detailed instructions, while another searching for 'best cake recipes' may be in the exploratory phase of a purchase decision.
Decoding search intent allows marketers and bloggers to deliver value that resonates with users. When you align your content with the intent behind the queries, you not only improve your chances of ranking higher but also enhance the user experience. To effectively determine user intent, consider utilizing tools like keyword research and analytics to uncover what your audience is truly after. By addressing search intent directly, you position your content as the solution to users' problems, ultimately leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.